Case studies
We’d love to talk you through the cool things we’ve done over the last 20 years! Here is a sample of a few ways we’ve applied UX and human factors research and design methods.
Explore our areas of expertise:

A health app company focused on female health wanted to evaluate compliance with accessibility standards to provide an inclusive experience for all users.

A wearable technology company wanted to understand the current telehealth landscape in hopes of identifying unexpected insights about the future of telehealth, particularly in the age of COVID-19.
A pharmaceutical manufacturer was interested in obtaining empirical data and user feedback regarding the usability of a medication delivery system, including the devices, labeling, and IFU.
A manufacturer of surgical products had developed a new surgical mesh that provided various advancements in clinical outcomes, but also came with necessary adjustments to implantation procedure.
A pharmaceutical company required a validation study to determine if the preparation and administration of an injection kit requiring the reconstitution of a pediatric medication was safe and effective.

A pharmaceutical manufacturer wanted to use an existing connected system mobile app with a pediatric population.
A pharmaceutical manufacturer was interested in collecting data to inform the development of a large-volume autoinjector and its accompanying IFU and labeling.

A healthcare company sought to compare their injection device with comparable ones on the market in order to determine if it is considered “state-of-the-art.”

A healthcare company wanted to identify existing workflows of their laboratory equipment across global markets and determine opportunities for usability improvement.

The FDA reached out to the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society (HFES) to assemble a team of experts to provide a training course for the Division of Medication Error Prevention and Analysis (DMEPA) from the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER).

A global medical device manufacturer wanted to promote internal awareness of and appreciation for best practices in the application of human factors engineering to medical device development.
A pharmaceutical manufacturer required a validation study to determine if an autoinjector and its related materials were safe and effective.

A manufacturer of personal care products sought to assess the ability of users to follow cleaning and disinfection protocols in a clinical setting.

A pharmaceutical manufacturer was developing an updated version of an existing, in-market system to help patients with medication adherence. As a connected medical system, both the existing product and new product had an accompanying mobile application.

A pharmaceutical manufacturer sought to improve the design and usability of a currently available pump carrying accessory.
A medical manufacturer had US-approved surgical equipment, but the current design was not working for some international markets.

A pharmaceutical company asked us to test the design preferences and usability of a mobile application designed as a 6-week treatment program to help patients manage their depression.

A medical device manufacturer asked us to evaluate the use of their hematology analyzers in different settings and identify opportunities for improvement.

An innovative healthcare solutions company sought to test the usability of their electronic health record (EHR) mobile application.
A pharmaceutical manufacturer was exploring next generation improvements for currently available medication to treat osteoarthritis in the knee.

A pharmaceutical company wanted to understand if potential functionalities of a digital therapy met user needs.
A pharmaceutical manufacturer was simultaneously developing a liquid formulation for a drug (currently only available as a pill), as well as a new delivery device to administer this liquid formulation.
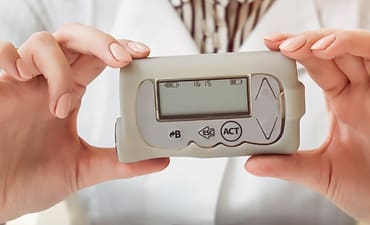
A pharmaceutical manufacturer sought to explore the ideal customer journey for a new connected wearable medication delivery system.

A pharmaceutical company planned to make an existing infusion pump available to a new patient population.

A pharmaceutical manufacturer wanted to eliminate selection errors due to similar packaging.

A global healthcare company sought to improve speech detection algorithms used by health care professionals (HCPs) to access patient information.

A pharmaceutical company needed to test usability of an app for patients facing a serious medical condition.

A global biotechnology company wanted to assess the usefulness and usability of its informational website designed for clinicians.

A medical device manufacturer sought to evaluate the usability and safety of the patch pump and training with potential patients and healthcare providers.

A medical device manufacturer asked us to evaluate the usability of a home monitoring device for individuals with pacemakers and defibrillators and explore ways to improve the product according to user needs and preferences.

A developer of digital health self-assessment tools sought usability testing for an innovative smartphone app designed to help healthcare professionals and patients better understand MS.

A Fortune 50 healthcare organization was developing an AI-enabled electronic medical record designed to improve providers’ situational awareness, communication, collaboration, and response.

A pharmaceutical company needed to evaluate the effectiveness of their instructions for use for a new product.

A medical device manufacturer sought HF engineering support to develop HFE deliverables and conduct a validation study for an aesthetics device.

A healthcare company sought HFE support in the development of an HF plan for a drug/device combination product and its accompanying IFU.

A pharmaceutical manufacturer wanted to improve the usability and usefulness of an existing HCP portal for a desktop and design a new mobile app version of the portal.

A manufacturer of surgical and delivery devices needed to better understand use cases around the deployment of their crash cart products in typical clinical environments.

A pharmaceutical company sought to understand how people with diabetes use technology to manage their disease.